Executive summary:
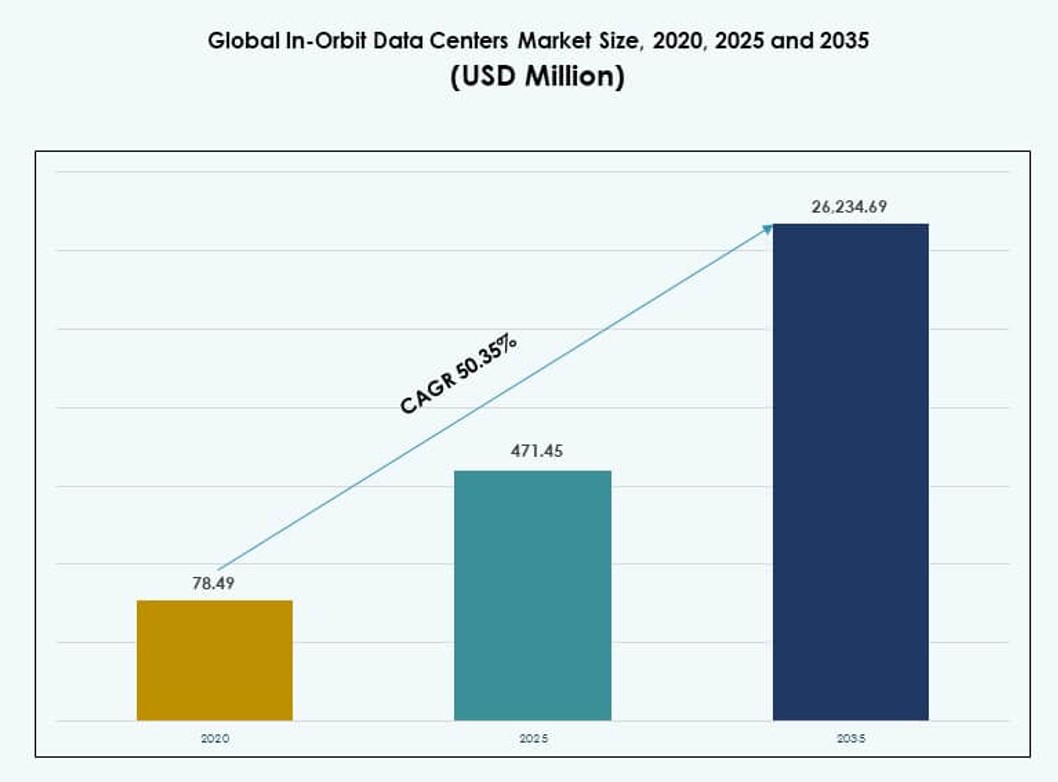
The Global In-Orbit Data Centers Market size was valued at USD 78.49 million in 2020 to USD 471.45 million in 2025 and is anticipated to reach USD 26,234.69 million by 2035, at a CAGR of 50.35% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2035 |
| In-Orbit Data Centers Market Size 2025 |
USD 471.45 Million |
| In-Orbit Data Centers Market, CAGR |
50.35% |
| In-Orbit Data Centers Market Size 2035 |
USD 26,234.69 Million |
The Global In-Orbit Data Centers Market grows due to rising demand for real-time data processing in space. Satellite operators adopt onboard computing to reduce latency and downlink loads. Advances in AI, edge computing, and radiation-hardened hardware support this shift. Commercial space activity accelerates deployment plans. Defense and scientific missions rely on secure in-orbit analytics. Businesses view this market as strategic digital infrastructure. Investors see strong long-term returns from early participation.
The Global In-Orbit Data Centers Market shows strong regional leadership in North America, led by the United States. The region benefits from advanced aerospace capabilities and public-private partnerships. Europe follows with active support from space agencies and research institutions. Asia Pacific emerges quickly, driven by China, Japan, and India. These countries expand satellite programs and local manufacturing. Other regions adopt gradually through collaborations and cost-focused deployments.
Market Dynamics:
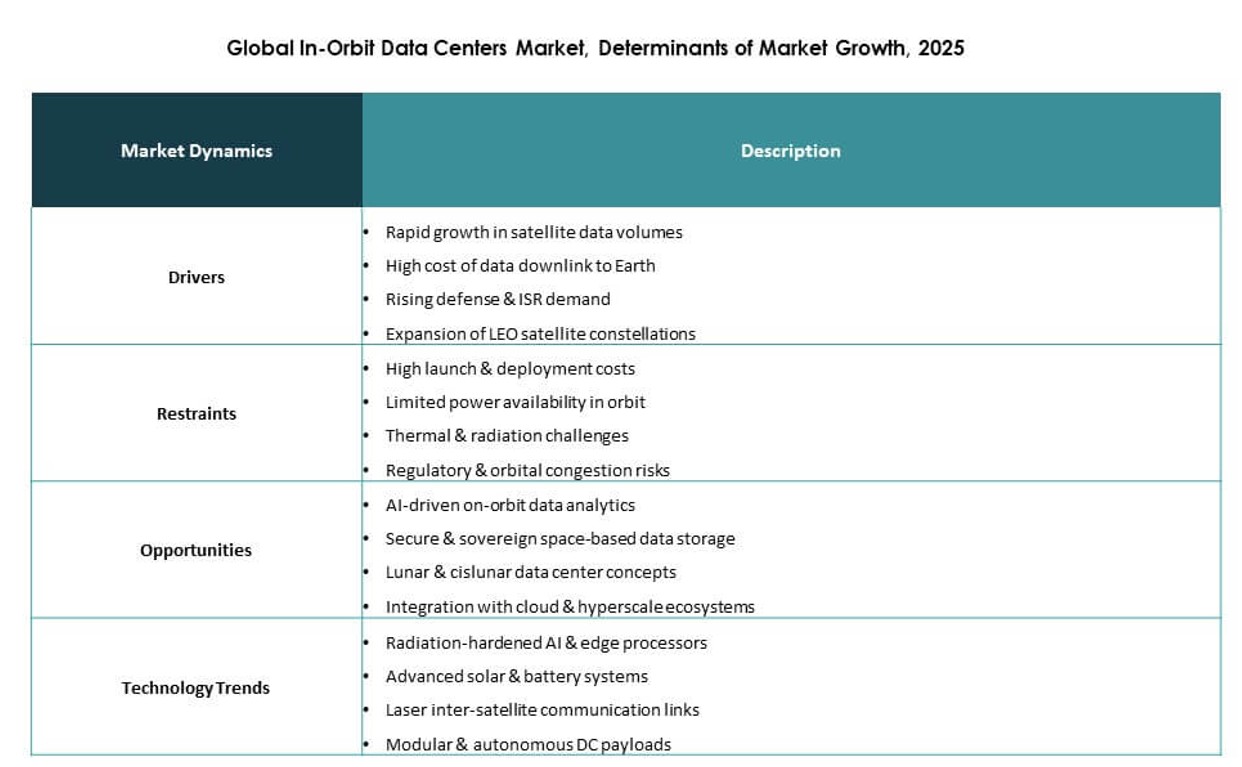
Market Drivers
Rapid Adoption of Edge Computing and Real-Time Data Processing in Space Missions
The Global In-Orbit Data Centers Market gains momentum from the growing demand for real-time data analytics and edge computing in satellite operations. Space agencies and commercial operators require immediate insights from Earth observation, telemetry, and scientific experiments. In-orbit data centers enable on-site processing, reducing latency and bandwidth dependence. This shift optimizes mission outcomes and improves responsiveness. Government contracts and defense applications further boost investments. By processing data directly in orbit, businesses avoid downlink bottlenecks. The infrastructure supports next-gen communications, autonomous space robotics, and AI workloads. It becomes a core enabler of advanced space technologies.
Accelerating Investments from Private Space Tech Companies and Public-Sector Collaborations
Rising investments from aerospace giants, startups, and venture capital firms drive technology innovation. Firms like Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman, and Microsoft explore space-grade cloud and compute platforms. Public-private partnerships help lower launch costs and ease regulatory pathways. Strategic alliances between space tech and data infrastructure firms open new commercialization models. The Global In-Orbit Data Centers Market benefits from stronger funding pipelines and government support. Use cases in surveillance, climate monitoring, and disaster management attract institutional interest. Investors view space-based compute as a long-term infrastructure play. Early movers position themselves as future digital backbones of orbital ecosystems.
- For instance, Starcloud launched the Starcloud‑1 satellite in 2025 carrying an NVIDIA H100 GPU, marking the first deployment of this class of AI accelerator in orbit. The satellite successfully demonstrated in‑orbit AI model execution, validating the feasibility of high‑performance computing for space‑based data processing.
Breakthroughs in Radiation-Hardened Computing and Compact Modular Architecture
Advanced computing hardware designed for space resilience fuels innovation. Vendors develop radiation-hardened processors, thermal control systems, and modular chassis for harsh environments. These breakthroughs enable durable, repairable, and scalable infrastructure in orbit. Compact designs fit payload constraints of launch vehicles. Companies integrate AI accelerators, GPUs, and high-density storage in small form factors. The Global In-Orbit Data Centers Market grows with maturing hardware ecosystems. It allows broader participation from cloud providers and edge analytics firms. Space-grade systems now support continuous processing without degradation. These advances unlock new levels of mission autonomy and reduce dependency on ground stations.
Strategic Value in Enabling Sovereign and Decentralized Digital Infrastructure
In-orbit data centers offer a path to sovereign, decentralized, and resilient data networks above national territories. Countries and corporations seek to reduce exposure to terrestrial disruptions. Edge processing in orbit supports secure communications, critical systems, and satellite-to-satellite connectivity. It supports global coverage and instant access to remote operations. The Global In-Orbit Data Centers Market plays a strategic role in building future-proof digital infrastructure. Defense, logistics, telecom, and earth science sectors rely on this capacity. Data localization and operational control become achievable across geopolitical boundaries. This positions in-orbit compute as essential for national security and commercial continuity.
- For instance, NASA’s Mars Odyssey orbiter has remained active in Mars orbit for over 24 years since 2001, operating on an IBM RAD6000 processor with the VxWorks real-time OS. It serves as a critical communications relay for surface missions like Curiosity and Perseverance and has contributed to climate mapping and subsurface water detection.
Market Trends
Proliferation of Low Earth Orbit (LEO) Constellations Enhancing In-Orbit Compute Relevance
The rise of LEO satellite constellations boosts the need for distributed compute nodes in orbit. Thousands of satellites require onboard processing to manage imaging, telemetry, and communications tasks. Centralized downlink models create delays and congestion. The Global In-Orbit Data Centers Market responds with decentralized edge solutions that process data at the source. Operators use AI-enabled modules to reduce payload-to-ground transmission. Demand for localized compute grows with real-time navigation, drone control, and maritime tracking. Satellite-to-satellite networking fosters mesh compute models. These trends accelerate onboard storage and compute requirements across LEO networks.
Shift Toward AI-Driven Operations and Onboard Inference Models
Operators now embed AI models into in-orbit infrastructure for decision-making and autonomous control. Inference engines detect anomalies, classify terrain, or prioritize mission tasks. AI helps optimize bandwidth, power, and compute cycles in constrained environments. The Global In-Orbit Data Centers Market evolves with AI-centric design for orbital edge use. Neural processing units and accelerators are integrated into rugged hardware. Smart analytics support object detection, threat identification, and environmental monitoring. These systems cut down ground station dependencies. AI-driven orchestration supports satellite clustering and mission adaptability in real-time.
Rising Demand for Disaster Resilience and Space-Based Data Redundancy
Organizations seek continuity solutions that remain operational during natural disasters, cyberattacks, or terrestrial outages. In-orbit data centers offer redundant infrastructure above atmospheric risks. Enterprises pursue orbital backup for critical data and applications. The Global In-Orbit Data Centers Market meets this demand through hardened platforms for recovery and business continuity. Edge data recovery from space becomes viable with growing storage capacities. Governments support orbital disaster resilience programs. The trend aligns with future moonbase and planetary network planning. This adds strategic value to space infrastructure in national security doctrines.
Growth in Lunar and Deep Space Missions Driving Extended In-Orbit Compute Needs
Lunar missions and Mars preparation drive demand for extended data center capabilities beyond Earth orbit. Agencies like NASA and ESA plan long-duration missions that require local compute and storage. The Global In-Orbit Data Centers Market prepares for these demands with autonomous processing models. Systems must operate independently, far from Earth-based control. Space-grade infrastructure handles mission telemetry, simulation, and communication relays. The need for real-time analytics on lunar and planetary surfaces grows. In-orbit data centers form the digital layer of off-Earth operations. This long-horizon trend influences hardware and protocol development.
 `
`
Market Challenges
Complex Engineering Demands and Harsh Operating Conditions in Orbital Environments
Deploying data centers in space presents significant design and environmental challenges. Systems must withstand radiation, vacuum, thermal fluctuations, and launch shock. Cooling becomes difficult without convection. Developers need specialized materials, shielding, and fault-tolerant architectures. The Global In-Orbit Data Centers Market faces engineering hurdles in balancing power efficiency, hardware density, and operational longevity. Maintenance is rarely possible after deployment. Any malfunction risks mission success and large sunk costs. Testing cycles extend product timelines. These factors increase entry barriers for smaller firms and raise capital requirements for innovation.
Regulatory Uncertainty and Limited Standards for Orbital Data Infrastructure
Lack of standardized regulations for in-orbit computing creates legal and operational uncertainty. Cross-border data handling in space remains undefined in many jurisdictions. Operators must navigate fragmented space laws, spectrum rights, and cybersecurity frameworks. The Global In-Orbit Data Centers Market needs unified policies on data jurisdiction, sovereignty, and compliance. Insurance, liability, and dispute resolution remain grey areas. The absence of orbital data governance slows commercial scaling. Harmonizing space and digital regulations requires multilateral engagement. Until clearer frameworks emerge, deployment risk stays high for commercial entrants.
Market Opportunities
Emerging Commercial Models for Data-as-a-Service from Space Infrastructure
Data center operators can monetize storage, processing, and analytics capabilities from orbit. New business models include satellite-as-a-service, AI-on-demand, and sovereign data vaults. The Global In-Orbit Data Centers Market enables telecom, cloud, and defense sectors to access orbital compute without owning physical assets. Flexible, pay-per-use platforms open doors for SMEs and startups. Growth in climate tech, agri-tech, and maritime surveillance drives service diversity. Modular systems support incremental scaling and faster time to market.
Strategic Expansion into Space-Based Cloud and Hyperscale Integration
Major cloud providers explore space-based data layers to extend coverage and improve latency. Partnerships with satellite operators unlock hybrid cloud services across terrestrial and orbital zones. The Global In-Orbit Data Centers Market provides a new frontier for hyperscale growth. Providers aim to integrate in-orbit compute into global network fabrics. This supports seamless data handoffs and resilient architectures. National cloud policies also drive sovereign orbital deployments for secure workloads.
Market Segmentation:
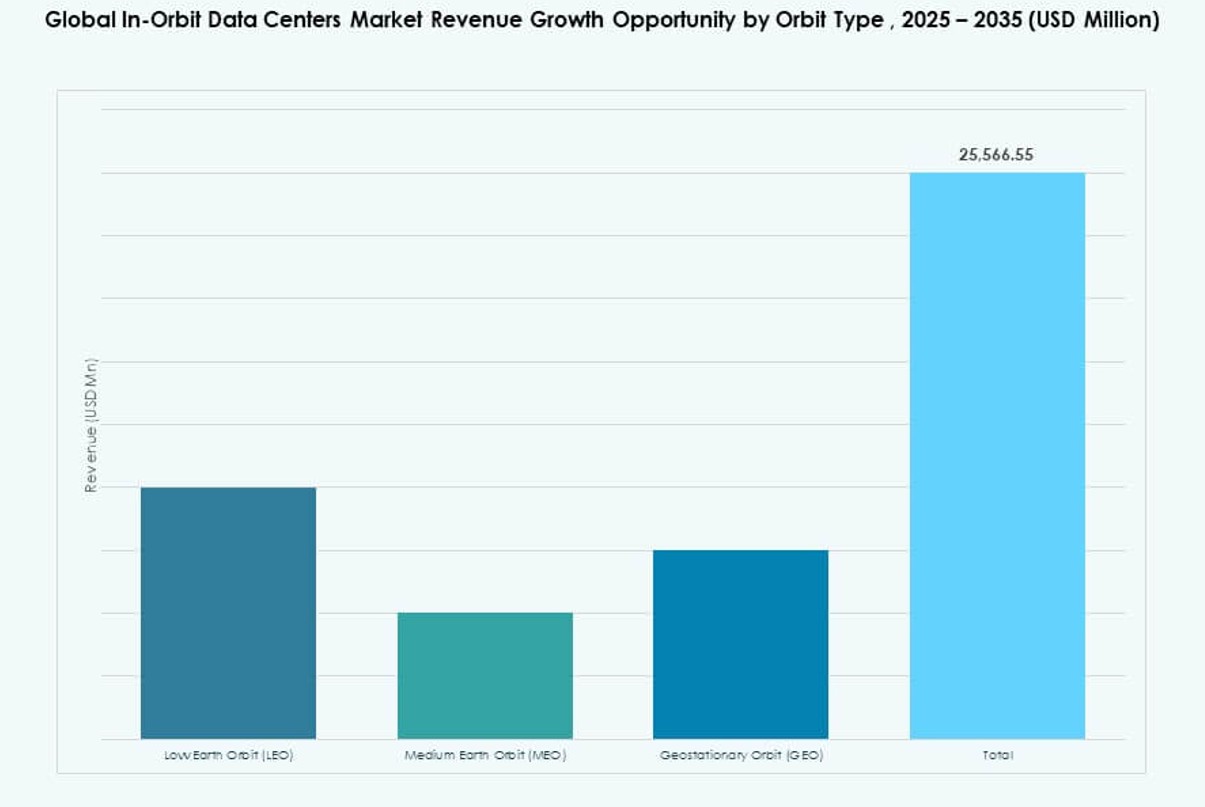
By Orbit Type
In the Global In‑Orbit Data Centers Market, Low Earth Orbit (LEO) holds the dominant share due to the proliferation of small satellites and mega constellations that demand onboard processing. LEO’s lower latency and reduced launch cost make it ideal for real‑time data handling, remote sensing, and communications. Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) is rising with navigation and telecom applications. Geostationary Orbit (GEO) still supports large payload missions but grows slower. Growth drivers include lower latency, frequent revisit rates, and reduced dependency on ground links.
By Data Center Type
Edge / Distributed In‑Orbit Data Centers leads the market as operators seek distributed compute closer to data sources for faster responses. This segment captures the largest share by enabling real‑time analytics and reducing data transfers to Earth. Modular In‑Orbit Data Centers follow, offering scalable deployment and easier integration with different satellite buses. Hosted Payload Data Centers attract niche use for shared platforms. Drivers include mission flexibility, plug‑and‑play modularity, and reduced latency for time‑critical applications.
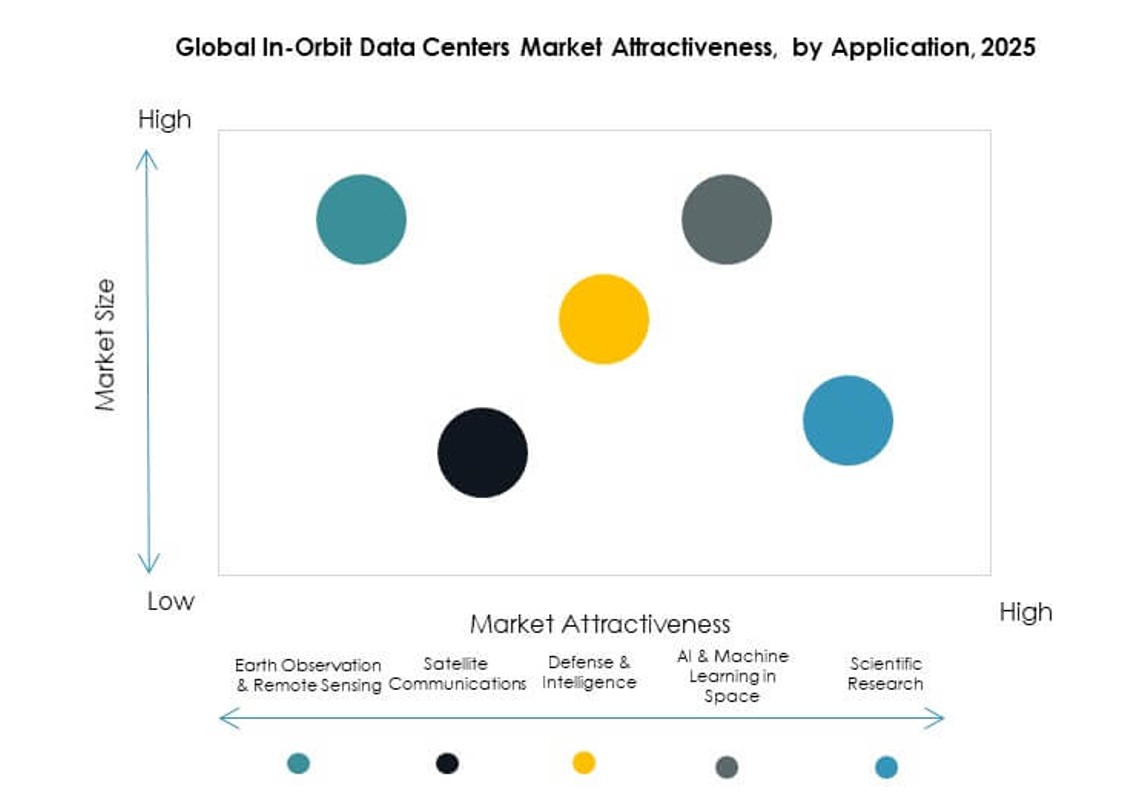
By Application
Earth Observation & Remote Sensing is the foremost application segment in the Global In‑Orbit Data Centers Market, propelled by demand for high‑resolution imaging and environmental analytics. Satellite Communications also commands significant share due to increasing broadband demand and connectivity needs. Defense & Intelligence is a high‑growth segment with secure, low‑latency processing needs. AI & Machine Learning in Space and Scientific Research are emerging as key drivers, leveraging in‑orbit processing to reduce data downlink burden and accelerate mission insights.
By End‑user
Government & Defense Agencies dominate the Global In‑Orbit Data Centers Market with the largest share, driven by national security, space exploration, and strategic infrastructure goals. Commercial Satellite Operators follow, investing to enhance service offerings and onboard processing efficiency. Cloud & Hyperscale Providers are expanding presence to extend edge services into orbit. Research Institutions occupy a smaller but growing segment, leveraging in‑orbit compute for scientific experiments and space science missions. Demand stems from secure data handling, real‑time insights, and sovereign infrastructure needs.
By Component
In the Global In‑Orbit Data Centers Market, Servers and Storage Systems capture the highest share due to essential roles in compute and data retention in orbit. Networking Devices are critical for satellite interconnectivity and data exchange. Antenna and Payload components support signal handling and mission‑specific tasks. Power Source segments, including solar and battery technologies, grow steadily with improved energy efficiency. “Others” include thermal controls and housing structures, which support overall system resilience. Growth factors include miniaturization, space‑grade certification, and reliability under extreme conditions.
Regional Insights:
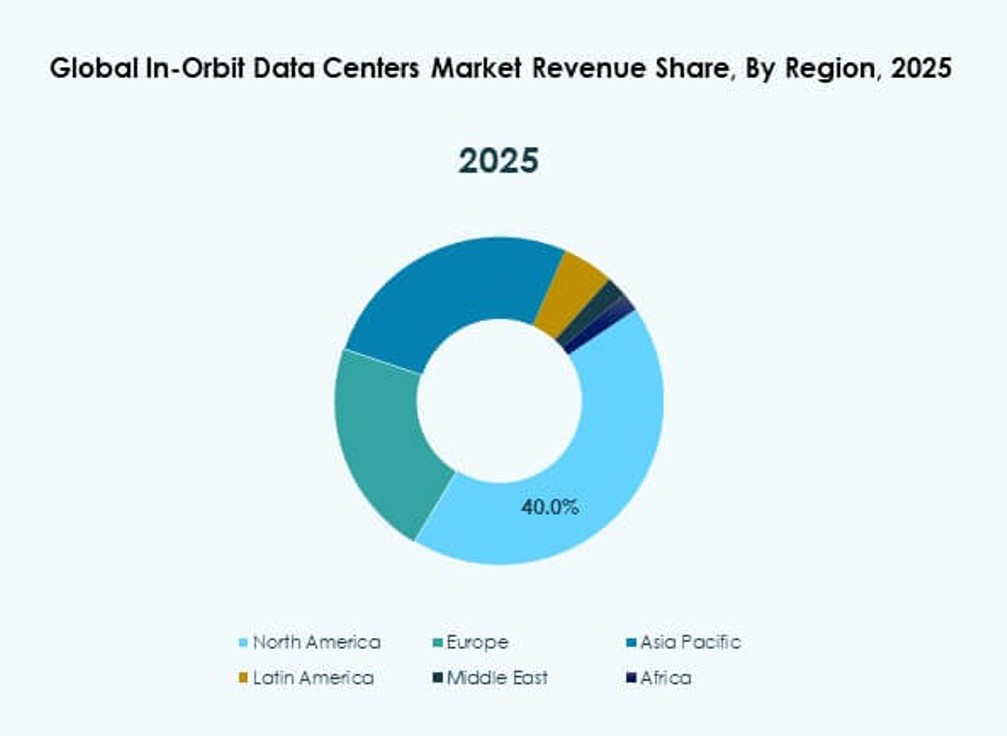
North America
North America holds the largest share at about 40% of the Global In‑Orbit Data Centers Market due to strong aerospace infrastructure and high R&D investment. The United States leads with government and commercial programs that accelerate orbital compute deployments. Canada supports satellite operations and space tech partnerships, though at smaller scale. Industry collaboration between defense, cloud providers, and satellite firms fuels adoption. Regulatory clarity and capital access strengthen market position. Higher launch frequency from regional spaceports also supports growth. Investors favor North America for its mature supply chain and innovation ecosystem.
Europe And Asia‑Pacific
Europe accounts for approximately 25% market share driven by active space agencies and multinational collaborations. Countries like France and Germany host key aerospace firms developing modular in‑orbit platforms. The European Space Agency (ESA) funds initiatives that advance compute and data handling in orbit. Demand rises from Earth observation and defense programs. Research institutions in Europe partner with industry to prototype new systems. Stable policy frameworks attract sustained investment. Europe’s focus on secure data infrastructure boosts regional uptake.
- For instance, the European Space Agency supports advanced onboard computers and data handling technologies that help spacecraft manage telemetry and payload data securely in orbit, and European aerospace firms contribute mission‑critical electronic systems for launch vehicles like Ariane 6.
Latin America, Middle East And Africa
Asia‑Pacific captures about 25% of the market, with China and Japan leading technology adoption and satellite manufacturing. South Korea and India expand space programs that adopt orbital data centers for communications. Australia supports space tech through government and private funding. Latin America holds roughly 5% share, driven by Brazil’s satellite initiatives. The Middle East also contributes near 3% with national space strategies in the GCC and Israel. Africa maintains around 2% with growing interest in remote sensing and connectivity projects. These regions focus on cost‑efficient solutions and partnerships to boost local capabilities.
- For instance, ISRO’s GSAT‑29 features high-throughput Ka and Ku-band transponders along with a Q/V-band payload and optical communication technology, enabling advanced satellite communications and demonstrating experimental high-speed data transmission capabilities for future missions.
Competitive Insights:
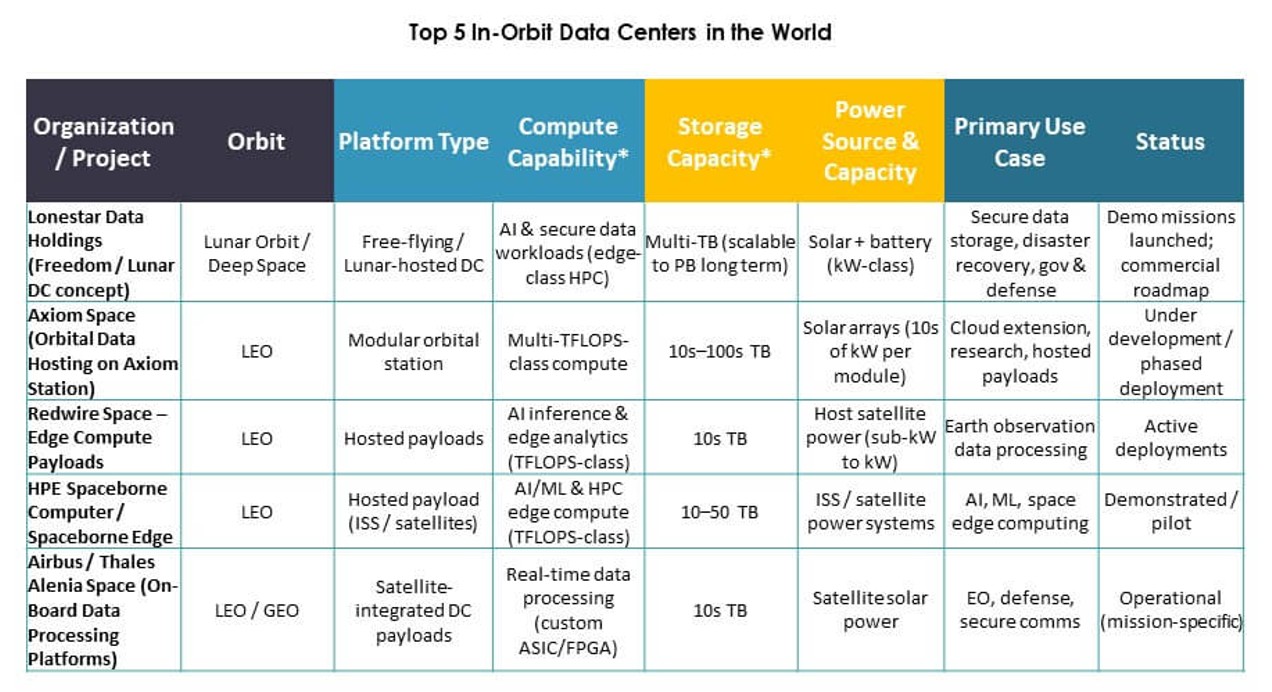
- Lonestar Data Holdings
- SpaceBilt
- Redwire Space
- Orbital Reef (Blue Origin consortium)
- Star Cloud, Inc.
- NTT Corporation
- Axiom Space, Inc.
- OrbitsEdge
- Skyloom
- SKY Perfect JSAT Holdings Inc.
- Kepler Communications Inc.
- KP Labs
- Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (AMD)
- NVIDIA Corporation
- IBM
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development LP
- National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA)
- European Space Agency (ESA)
The competitive landscape of the Global In‑Orbit Data Centers Market reflects a mix of traditional aerospace contractors, dedicated space tech innovators, and tech giants moving into orbit compute services. Established players like NASA and ESA drive standards, missions, and collaborations that shape technology paths. SpaceBilt, Lonestar Data Holdings, and Redwire Space push commercial deployment of modular and hosted payload data centers. Tech firms including AMD, NVIDIA, IBM, and Hewlett Packard Enterprise bring processing power and storage solutions tailored for space environments. Satellite ecosystem firms such as SKY Perfect JSAT Holdings and Kepler Communications extend operational networks. OrbitsEdge, Axiom Space, and Skyloom focus on network and service platforms. NTT Corporation leverages telecom strength for global data integration. Competitive strategies include partnerships, technology alliances, and platform diversification to capture future in‑orbit infrastructure demand.
Recent Developments:
- In December 2025, PowerBank Corporation announced the successful launch of the DeStarlink Genesis-1 satellite in partnership with Orbit AI (Smartlink AI), initiating the Orbital Cloud project for decentralized low-Earth orbit networks combining AI compute, blockchain, and solar power.
- In November 2025, Starcloud launched its Starcloud-1 satellite carrying an Nvidia H100 GPU, marking the first demonstration of training an AI model like Google’s Gemma in orbit, as part of efforts to advance in-orbit data centers for AI workloads.
- In September 2025, Axiom Space and SpaceBilt announced a collaboration to deploy the Axiom Orbital Data Center Node on the International Space Station, an optically interconnected high‑performance orbital data center node that will enable satellites, other spacecraft in low Earth orbit, and ISS users to store and process data and run AI/ML and cloud workloads in space as part of Axiom’s broader in‑orbit data center strategy.
- In April 2025, Kepler Communications Inc. introduced a new on‑orbit compute capacity offering on its optical data relay constellation, The Kepler Network, allowing customers to lease or purchase computing hardware on its satellites to perform advanced processing, data storage, cloud compute, AI, and multi‑sensor data fusion in space, effectively providing in‑orbit data center capabilities.

 `
`


