Executive summary:
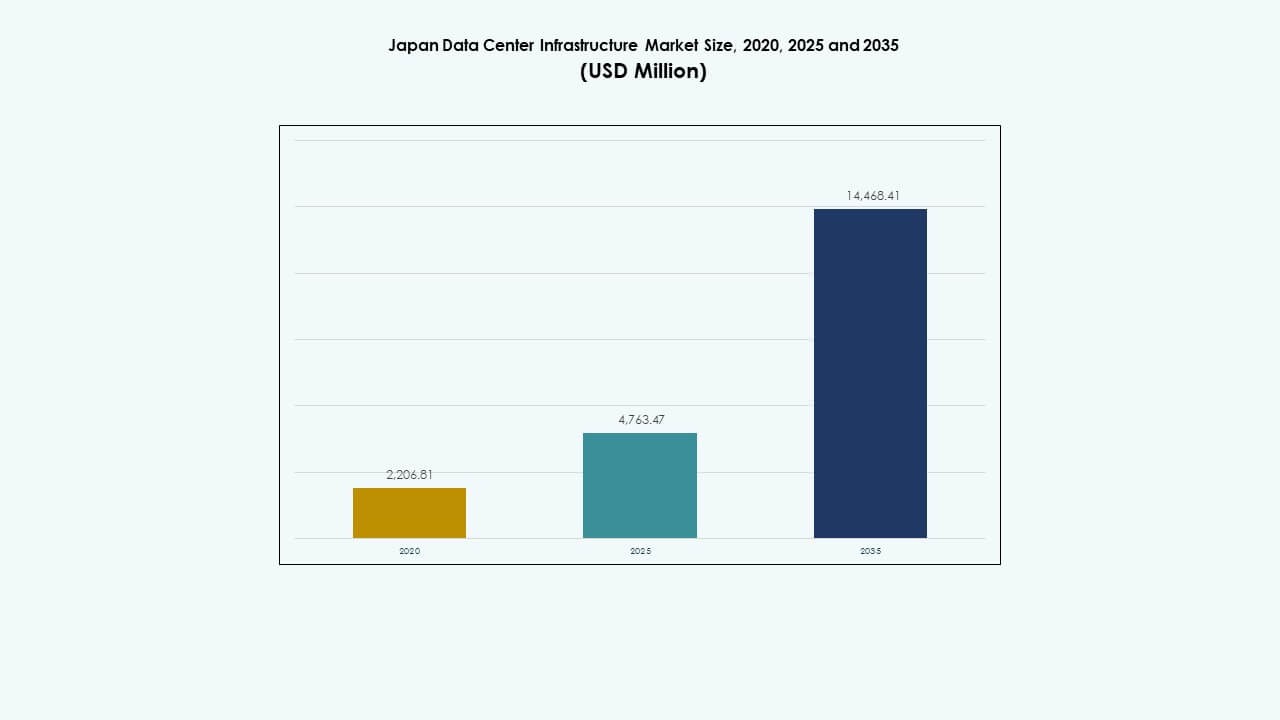
The Japan Data Center Infrastructure Market size was valued at USD 2,206.81 million in 2020 to USD 4,763.47 million in 2025 and is anticipated to reach USD 14,468.41 million by 2035, at a CAGR of 11.65% during the forecast period.
| REPORT ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
| Historical Period |
2020-2023 |
| Base Year |
2024 |
| Forecast Period |
2025-2035 |
| Japan Data Center Infrastructure Market Size 2025 |
USD 4,763.47 Million |
| Japan Data Center Infrastructure Market, CAGR |
11.65% |
| Japan Data Center Infrastructure Market Size 2035 |
USD 14,468.41 Million |
Growing AI adoption, 5G deployment, and cloud migration are reshaping infrastructure needs across industries. Hyperscale and colocation operators invest in scalable, energy-efficient systems to support high-density and latency-sensitive workloads. Innovation in cooling, modular construction, and energy management enhances performance and sustainability. Businesses value these assets for their long-term stability and low operational risk. For investors, the Japan Data Center Infrastructure Market offers durable returns, steady demand, and alignment with national digital transformation goals.
Tokyo and Yokohama dominate the market due to strong enterprise activity, high connectivity, and hyperscaler presence. Osaka serves as a key secondary hub, driven by manufacturing, finance, and logistics. Emerging regions like Hokkaido and Kyushu attract investment for their land availability, renewable energy, and lower operational costs. These areas support Japan’s shift toward edge computing and regional data resilience. This geographic spread strengthens the overall infrastructure ecosystem.
 Market Drivers
Market Drivers
Strong Cloud Integration and Demand for Scalable Infrastructure Among Japanese Enterprises
Japan’s enterprise sector shows accelerated migration to public and hybrid cloud models. Businesses demand highly scalable and secure data center environments to support AI, IoT, and analytics. This has led to a spike in hyperscale and colocation infrastructure investments. Operators focus on power redundancy, network resilience, and fault tolerance. The Japan Data Center Infrastructure Market benefits from predictable long-term leasing by global hyperscalers. IT modernization is central to digital competitiveness across sectors. Financial services and e-commerce firms drive a large share of demand. Strategic positioning ensures stable occupancy rates and favorable investor returns.
- For instance, Colt Data Centre Services launched Inzai‑3 in 2020 with 8,000 square meters of white space and Tier 3‑equivalent redundancy featuring dual power feeds. This has led to a spike in hyperscale and colocation infrastructure investments.
Edge Computing and 5G Rollout Reinforce Infrastructure Demand Beyond Core Urban Clusters
Japan’s national 5G rollout is triggering demand for decentralized edge infrastructure. Data center operators are deploying compact, high-density edge nodes near user populations. These installations reduce latency and support real-time analytics for autonomous systems and IoT. The Japan Data Center Infrastructure Market is shifting toward a distributed design model. Automotive and smart city projects anchor regional edge investments. Tier 2 cities attract deployments due to power availability and lower land costs. Edge growth complements core colocation hubs in Tokyo and Osaka. Network densification and edge coverage enable low-latency digital services nationwide.
Innovation in Cooling, Energy Optimization, and Modular Systems
Next-generation cooling systems reduce energy use in high-density server environments. Operators adopt direct-to-chip liquid cooling and AI-driven thermal control. The Japan Data Center Infrastructure Market shows strong traction in sustainable, high-efficiency designs. Modular construction speeds deployment and minimizes environmental impact. Government incentives promote renewable energy use in data centers. Japan’s geographic constraints push innovation in vertical and underground data centers. Efficient building practices help reduce PUE scores. These trends enhance competitiveness while aligning with ESG objectives.
- For instance, NTT’s Shiroi-1 Data Center near Tokyo is designed to deliver 24 MW of IT load across 7,360 square meters of server space. It is part of a major hyperscale campus aimed at supporting enterprise and cloud growth in Japan.
Strategic Investment from Global Cloud Providers and Domestic Telecom Giants
Amazon Web Services, Google, Microsoft, and Alibaba expand their Japan cloud zones. Domestic leaders like NTT Communications and SoftBank invest in hyperscale and submarine cable capacity. The Japan Data Center Infrastructure Market supports long-term investment horizons and regulatory clarity. Partnerships between real estate developers and digital infra specialists grow. Real asset managers and sovereign funds show rising interest in the market. High entry barriers ensure low volatility and durable income for institutional investors. Japan’s geopolitical stability supports its role as a Northeast Asia digital hub.
 Market Trends
Market Trends
AI-Optimized Infrastructure and Growing Use of GPU-Based Server Farms
AI model training and inference require massive compute power. Demand for GPU-powered clusters drives new infrastructure design. The Japan Data Center Infrastructure Market sees rapid deployment of AI-ready facilities. Operators invest in high-power-density racks and reinforced cooling systems. Enterprises seek AI-as-a-service platforms hosted locally. GPU demand outpaces traditional CPU-based capacity. Use cases range from manufacturing and logistics to fintech and gaming. Facilities are tailored for heat dissipation and fast parallel processing.
Shift Toward Renewable Energy Sourcing and Carbon-Neutral Facility Targets
Operators target carbon-neutral operations by 2030 or earlier. Solar, wind, and hydro partnerships support sustainable data center builds. The Japan Data Center Infrastructure Market aligns with the government’s Green Growth Strategy. Colocation providers offer green-certified facilities to attract ESG-conscious clients. Data centers invest in carbon offset programs and on-site solar arrays. Energy storage systems stabilize renewable supply variability. Firms adopt green building certifications like CASBEE and LEED. Cleaner grids and advanced cooling reduce carbon footprint.
Advanced Security and Zero-Trust Architecture Driving Infrastructure Overhauls
Cybersecurity threats reshape physical and digital architecture priorities. Operators implement zero-trust frameworks and multi-factor access control. The Japan Data Center Infrastructure Market responds with infrastructure hardened for secure workloads. Clients demand high-level certifications including ISO/IEC 27001 and SOC 2. Physical access systems integrate biometrics and AI-based monitoring. Encrypted fiber and secure routing technologies gain adoption. Government agencies and defense clients require sovereign infrastructure control. The market sees convergence of IT and physical security layers.
Integration of Smart Building Management and Predictive Maintenance Tools
Facility operations now use digital twins and AI analytics for equipment maintenance. Smart BMS platforms track airflow, humidity, and energy consumption in real time. The Japan Data Center Infrastructure Market deploys condition-based maintenance to reduce downtime. Sensors provide granular data for performance optimization. Predictive tools cut repair costs and boost reliability. Operators monitor vibration, thermal variance, and power fluctuation. These tools support compliance, safety, and ESG transparency. Automation reduces OPEX and labor dependencies.
 Market Challenges
Market Challenges
Power Supply Constraints, Grid Limitations, and Energy Pricing Pressures
Power availability remains a top constraint for hyperscale expansion in urban areas. Tokyo faces capacity bottlenecks due to grid congestion and limited substation space. The Japan Data Center Infrastructure Market faces rising electricity prices from global LNG volatility. Delays in new grid infrastructure slow site selection. Operators shift focus to energy storage and hybrid generation solutions. Permitting for new high-voltage lines adds development risk. Urban zoning limits the scope for on-site generation. These pressures raise project CAPEX and operating cost ratios.
Land Scarcity, Natural Disaster Risk, and Construction Cost Escalation
Land availability is limited, especially in metro regions like Tokyo and Yokohama. Earthquake and typhoon resilience requires premium design features. The Japan Data Center Infrastructure Market faces structural hardening costs and seismic retrofitting needs. Construction timelines extend due to skilled labor shortages and regulatory compliance. Vertical builds and underground models offset land constraints but raise cost. Earthquake-resistant materials and backup systems inflate budgets. Operators must factor in site redundancy and recovery planning. Long permitting cycles affect market agility.
Market Opportunities
Expansion in Edge Zones and Untapped Regional Areas for Decentralized Infrastructure
Emerging cities offer attractive conditions for edge deployment. Kyushu, Hokkaido, and Shikoku present land availability, renewable power access, and lower costs. The Japan Data Center Infrastructure Market shows potential beyond Tokyo-Osaka corridor. Smart city and 5G expansion will anchor future edge data nodes. Regional universities and innovation hubs may create localized demand. Government grants and private partnerships could accelerate regional development. Edge zones offer strategic advantage for CDN and real-time apps.
Digital Sovereignty, Government Cloud Mandates, and National AI Strategy Alignment
Government-backed digital programs support localized, sovereign data storage mandates. The Japan Data Center Infrastructure Market benefits from public cloud expansion aligned with national AI goals. Ministries invest in secure hosting for citizen data and critical systems. New AI laws emphasize local processing and data residency. Operators see opportunities in regulatory-compliant infrastructure for public sector clients. Sovereign cloud regions enhance resilience against geopolitical risk. These initiatives encourage public-private partnerships in next-gen data infra.
 Market Segmentation
Market Segmentation
By Infrastructure Type
The Japan Data Center Infrastructure Market is led by electrical infrastructure, driven by rising rack power density. Mechanical infrastructure is growing with advanced cooling needs. IT and network infrastructure remains essential for modernization, while civil and architectural components evolve with modular designs. Electrical systems account for a dominant share due to UPS and PDU demand.
By Electrical Infrastructure
Uninterruptible power supply (UPS) and power distribution units (PDUs) dominate the segment due to reliability requirements. Battery energy storage systems show fast growth with green backup initiatives. Grid connections remain key in Tier 1 cities, while switchgear investments support new builds. UPS systems offer scalable redundancy, driving procurement across colocation and hyperscale setups.
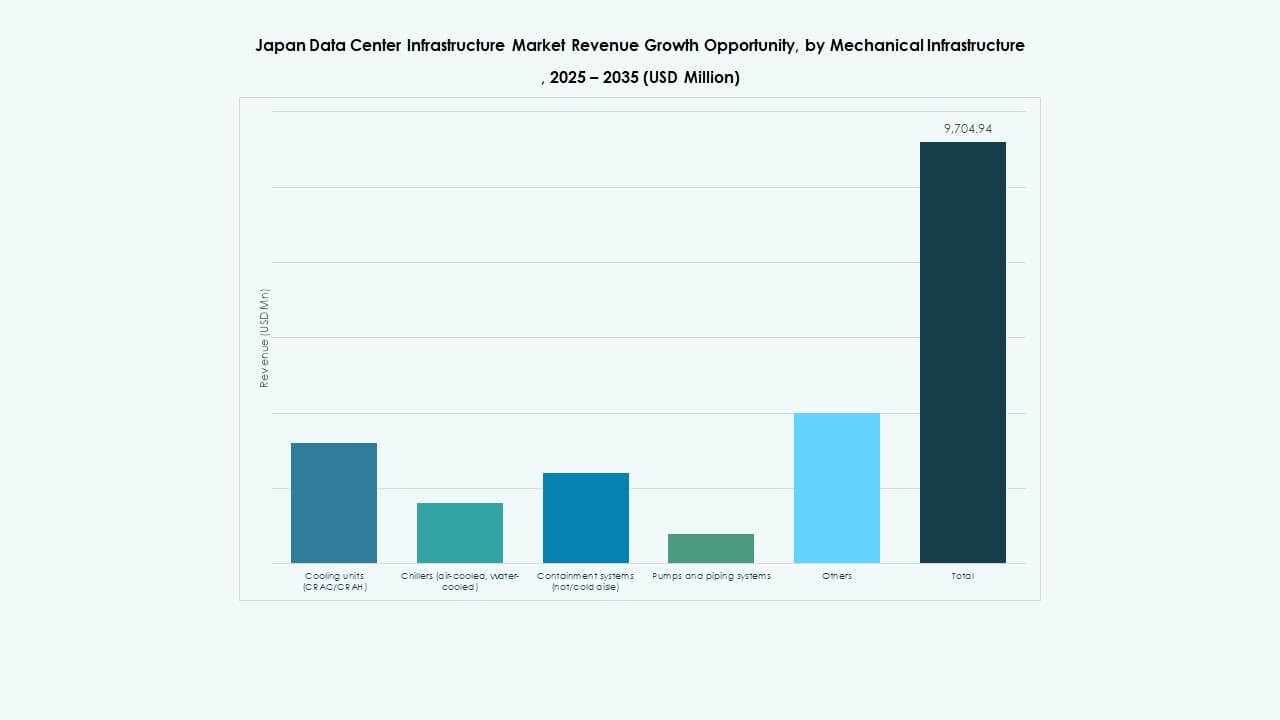
By Mechanical Infrastructure
Cooling units and chillers are essential due to the rise in AI and GPU workloads. The segment is shifting toward direct liquid cooling and containment strategies. Modular pump systems support flexible data hall layouts. The Japan Data Center Infrastructure Market sees growing investment in energy-efficient mechanical systems with predictive thermal control.
By Civil / Structural & Architectural
Modular building systems and raised floors dominate this segment, enabling faster and cost-efficient rollouts. Superstructures are reinforced for seismic resilience, especially in Tokyo and Kansai. Operators favor prefab designs for time-to-market advantages. Structural design aligns with green building codes and renewable integration.
By IT & Network Infrastructure
Servers and networking equipment account for a major share. Demand for AI and cloud-native workloads accelerates server refresh cycles. Storage and optical fiber cabling support data-intensive applications. Racks and enclosures are tailored for high-density and airflow optimization. The segment reflects Japan’s high-tech and digital economy structure.
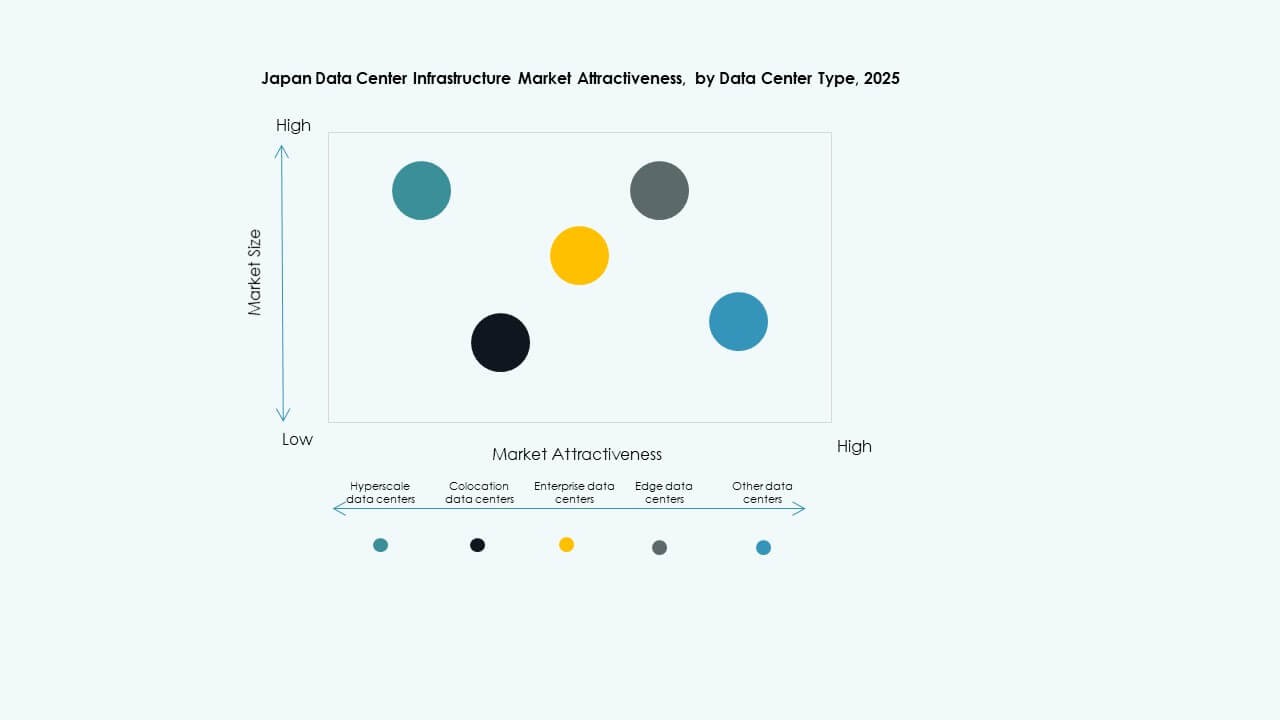
By Data Center Type
Hyperscale and colocation data centers dominate the market due to large enterprise and cloud workloads. Edge data centers grow in regional areas, while enterprise data centers see moderate demand. Hyperscale facilities support international platforms. The market aligns with cloud outsourcing and latency-sensitive application trends.
By Delivery Model
Turnkey and modular factory-built models lead due to speed and flexibility. Retrofit and upgrade projects support legacy facility transformation. EPC and construction management models are used in large, complex builds. The shift favors factory-assembled modules to minimize onsite complexity and risks.
By Tier Type
Tier 3 and Tier 4 facilities dominate due to demand for uptime and system resilience. Enterprise and financial clients prefer Tier 4 designs. Tier 2 deployments remain relevant in rural or edge setups. The Japan Data Center Infrastructure Market emphasizes redundancy and uptime guarantees.
Regional Insights
Kanto Region (Tokyo, Yokohama, Saitama) – Commanding Over 45% Market Share
The Kanto region leads due to dense enterprise activity, global connectivity, and hyperscaler presence. Tokyo remains the prime location for colocation and cloud nodes. High bandwidth, skilled labor, and financial institutions anchor growth. It faces land and power constraints but continues to attract large-scale investments. Government and telecom firms drive demand for sovereign infrastructure. Operators implement vertical and underground designs to optimize space.
- For instance, AWS operates 4 Availability Zones in its Asia Pacific (Tokyo) Region.
This is accurate. As of 2025, Amazon Web Services (AWS) confirms that its Asia Pacific (Tokyo) Region includes 4 Availability Zones, supporting scalable and resilient cloud services across Japan.
Kansai Region (Osaka, Kyoto, Kobe) – Securing Around 25% Market Share
Kansai is a strong secondary hub, supported by logistics, manufacturing, and research clusters. Osaka attracts hyperscale and disaster recovery deployments. The region benefits from strong power infrastructure and lower seismic risk zones. Colocation providers expand capacity in Osaka to serve western Japan. Kyoto and Kobe contribute through university research parks and tech firms. Redundancy between Tokyo and Osaka improves network resilience.
- For instance, Google Cloud launched its Osaka region in 2019 with 3 zones. Colocation providers expand capacity in Osaka to serve western Japan. Kyoto and Kobe contribute through university research parks and tech firms. Redundancy between Tokyo and Osaka improves network resilience.
Emerging Regions (Hokkaido, Kyushu, Chubu) – Combined Share Around 30%
Hokkaido and Kyushu offer low temperatures, renewable energy access, and ample land. These conditions favor green data center development. Chubu, home to Nagoya, supports growth from automotive and electronics industries. Operators explore edge zones for real-time services and AI inference. Local governments promote digital infrastructure through subsidies and zoning support. These regions help decentralize Japan’s data economy beyond traditional metros.
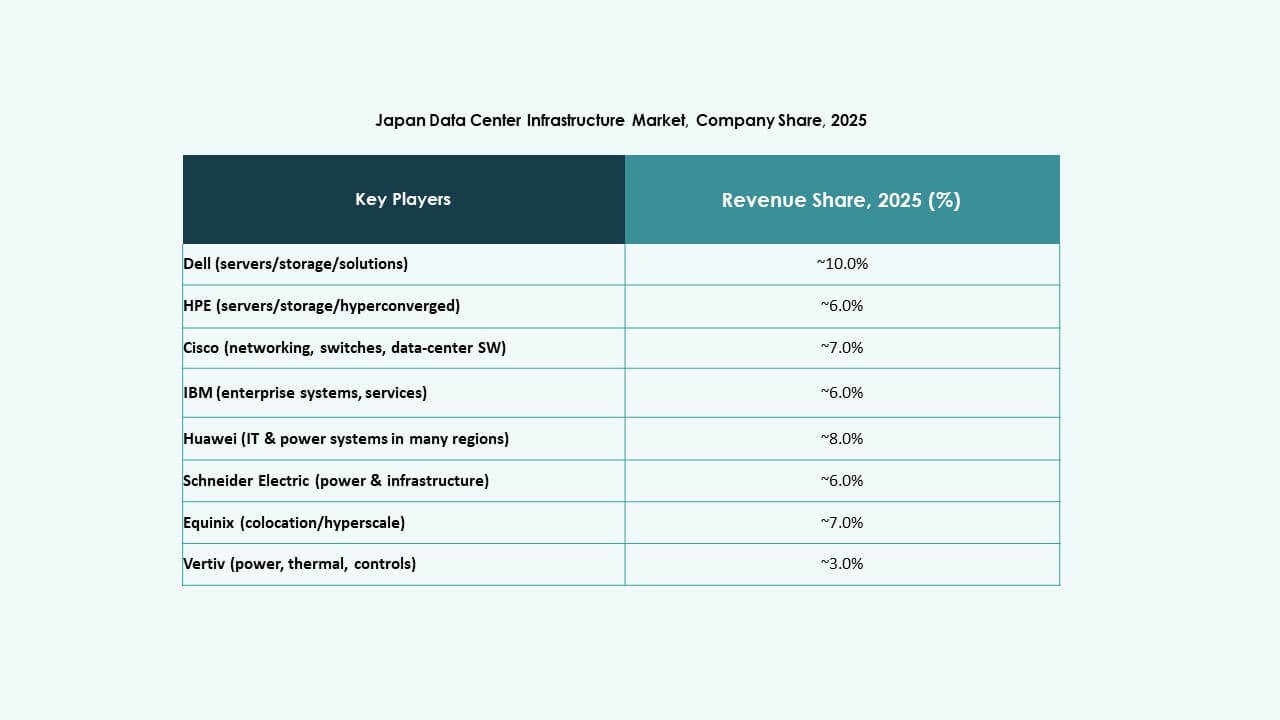
Competitive Insights:
- Schneider Electric
- Vertiv Group Corp.
- Fujitsu
- Hitachi, Ltd.
- Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
- Dell Inc.
- Equinix, Inc.
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- IBM
- ABB
The Japan Data Center Infrastructure Market features a mix of global infrastructure leaders, domestic technology giants, and specialized solution providers. Schneider Electric and Vertiv dominate power and cooling segments with scalable, energy-efficient systems. Fujitsu and Hitachi lead in integrated IT and facility management solutions, backed by deep local presence. Huawei and Dell offer advanced server and storage platforms supporting cloud and AI workloads. Equinix plays a key role in colocation infrastructure and interconnection services. Cisco and IBM contribute heavily to networking, automation, and security layers. ABB supports electrical infrastructure with grid-tied and modular components. The market encourages collaboration between telecom carriers, real estate developers, and tech firms. It demands innovation in energy use, space optimization, and regulatory compliance, creating opportunities for strategic partnerships and digital infrastructure transformation.
Recent Developments:
- In November 2025, Cisco Systems launched the Cisco Unified Edge appliance at its Partner Summit on integrating compute, networking, storage, and security to extend data center capabilities to network edges, enhancing AI and infrastructure support.
- In October 2025, ABB announced a collaboration with NVIDIA to develop gigawatt-scale next-generation AI data centers, focusing on high-efficiency 800 VDC power solutions for advanced AI workloads.
- In May 2025, Cummins partnered with AVAIO Digital to supply generators for backup power in upcoming AI-ready data centers, part of a $200 million equipment commitment delivered over 18 months to support high-density operations starting in 2026.
- In March 2025. Mitsui & Co. announced the acquisition of a 50% stake in an operational hyperscale data center in Japan In this deal, Mitsui’s subsidiary invested 18 billion yen through a holding company, marking a key expansion in their data center portfolio alongside institutional investors.
 Market Drivers
Market Drivers Market Trends
Market Trends Market Challenges
Market Challenges Market Segmentation
Market Segmentation